In a Perspective published in this week’s New England Journal of Medicine, Jessica Justman, Owen Mugurungi, and Wafaa El-Sadr show how Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (PHIA) data provide a robust picture of country-level HIV epidemics, including the gaps in the response, and help guide future actions with precision.
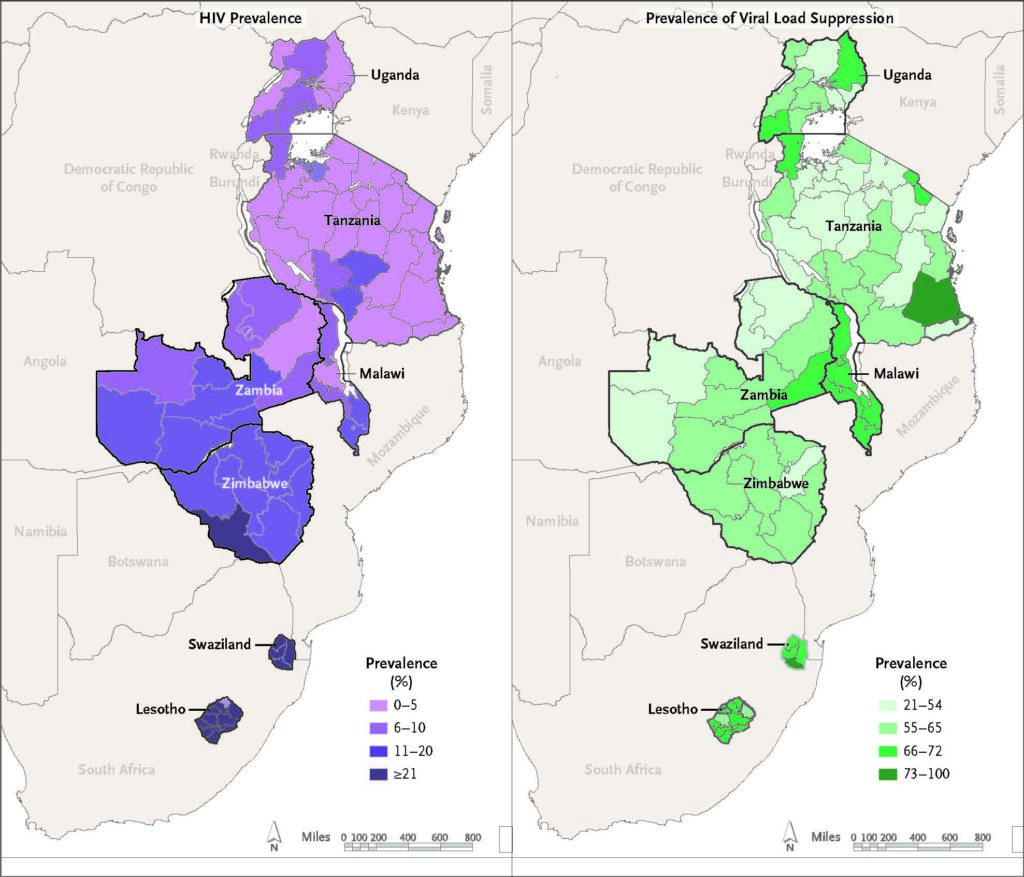
The article explains how PHIA surveys provide direct estimates of critically important measures, such as HIV incidence, population-level viral load suppression (defined as HIVRNA <1000 copies per milliliter), and other essential biomarkers countries and donors need to measure progress. Survey findings have revealed exceptional successes, such as a remarkably high prevalence of viral load suppression among adults living with HIV in three contiguous southern African countries (Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe).
See two new maps: HIV Prevalence and Prevalence of Viral Load Suppression in the NEJM article for a new revealing look at the data (Data in the article, from First Reports and preliminary Summary Sheets, are publically available at phia.icap.columbia.edu).
The article also details the value of repeated surveys, which can reveal trends over time, as demonstrated by comparing results from the Swaziland HIV Incidence Measurement Survey 2 (SHIMS2, 2017) with SHIMS (2011). SHIMS2 data showed a dramatic reduction in HIV incidence (44%) and doubling of population viral load suppression (from 35% to 71% among HIV-positive people aged 18 to 49 years).
The article concludes with an overview of the efforts required to plan and implement population surveys, and a call for more accurate and current population-level data in order to measure progress and guide future policy, programs, and funding decisions with precision. Read more at bit.ly/2L9z8Ky.
Jessica Justman is the Senior Technical Director and PHIA Project Principal Investigator at ICAP at Columbia University; Owen Mugurungi is the Aids and TB Unit director in the Ministry of Health and Child Care, Zimbabwe; Wafaa El-Sadr is the Global Director of ICAPat Columbia University.
Maps from New England Journal of Medicine, Jessica Justman, Owen Mugurungi, Wafaa El-Sadr, HIV Population Surveys – Bringing Precision to the Global Response, 378;20, 1859 Copyright © (2018) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission.
About the Population-based HIV Impact Assessment Project
The PHIA Project was launched in 2014 to address the need for detailed population HIVmeasures. Initial findings are already available from seven countries in sub-Saharan Africa (Zimbabwe, Malawi, Zambia, Swaziland, Lesotho, Tanzania, and Uganda), where approximately 200,000 individuals from more than 85,000 households have been surveyed. PHIA surveys are funded by PEPFAR and conducted by ICAP at Columbia University in partnership with ministries of health and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Online at phia.icap.columbia.edu.